`;^%��t� � 简介:
FRED作为COM组件可以实现与Excel、VB、
Matlab等调用来完成庞大的计算任务或画图,本文的目的是通过运行一个案例来实现与Matlab的相互调用,在此我们需要借助脚本来完成,此脚本为视为通用型脚本。
vWJ�hSpC[� GXEO��gf#i 配置:在执行调用之前,我们需要在Matlab命令行窗口输入如下命令:
z�N\~���v� enableservice('AutomationServer', true)
Q�7y6<�/4f enableservice('AutomationServer')
RRD\V3C�84 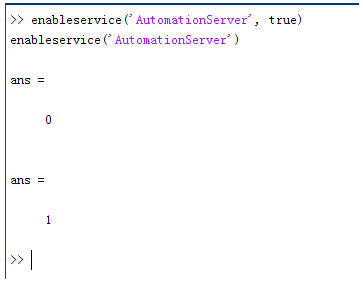 ��7eh|5e$@
��7eh|5e$@ 结果输出为1,这种操作方式保证了当前的Matlab实体可以用于
通信。
%Km_Sy[7']
/D�[�GXX� 在winwrp界面,为增加和使用Matlab类型的目录库,我们需要如下步骤:
tVhY=X{N�? 1. 在FRED脚本编辑界面找到参考.
Bc4{$�sc"O 2. 找到Matlab Automation Server Type Library
p6V`b'*>�� 3. 将名字改为MLAPP
�>#@��1
I� 6�'Sc�=;;: �5L<}u`�0J 在Matlab里面有两种常用的数据发送选项PutWorkspaceData 及PutFullMatrix,PutWorkspaceData适用于存储一般的数据在工作区,并赋予其为变量,PutFullMatrix试用于复数数据。
mI=^7�'Mk 图 编辑/参考
(BC3[�R@/l jl<rxO?-�F vf�@d��(g� 现在将脚本代码公布如下,此脚本执行如下几个步骤:
�9�Byk/&$U 1. 创建Matlab服务器。
@j$t���pz 2. 移动探测面对于前一聚焦面的位置。
�5� T��D�" 3. 在探测面追迹
光线 _"Q
�+G@@� 4. 在探测面计算
照度 ���E�<�3hy 5. 使用PutWorkspaceData发送照度数据到Matlab
�h^P>p�I�~ 6. 使用PutFullMatrix发送标量场数据到Matlab中
`8F%bc54iw 7. 用Matlab画出照度数据
FhB�^E$�r% 8. 在Matlab计算照度平均值
R�g��&6J#h 9. 返回数据到FRED中
x8�T�5a��S S�aE�e7eHd 代码分享:
|��}*��k�| do{#y*B/g! Option Explicit
k@5,6s:��
�DYH-5�yX7 Sub Main
b?o�T|��@� }>xgz�hd�T Dim ana As T_ANALYSIS
{K�L<Hx�2M Dim move As T_OPERATION
Do(7Li�dC5 Dim Matlab As MLApp.MLApp
�2
G_*�Pqc Dim detNode As Long, detSurfNode As Long, anaSurfNode As Long
�J
p� .w�g Dim raysUsed As Long, nXpx As Long, nYpx As Long
ewgcpV|spn Dim irrad() As Double, imagData() As Double, reals() As Double, imags() As Double
yX�N��E2K� Dim z As Double, xMin As Double, xMax As Double, yMin As Double, yMax As Double
��Q�8M&�nf Dim meanVal As Variant
�',0~��\�V �UD�*#�!H� Set Matlab = CreateObject("Matlab.Application")
!EM21�S��c `QR2!W70o3 ClearOutputWindow
}�i/�&m&VU >qx~m>2|8] 'Find the node numbers for the entities being used.
dv%gmUUf}k detNode = FindFullName("Geometry.Screen")
�AE�i@t0By detSurfNode = FindFullName("Geometry.Screen.Surf 1")
'N��5qX>Ob anaSurfNode = FindFullName("Analysis Surface(s).Analysis 1")
q4 'x�'8�� q �y�y.3-( 'Load the properties of the analysis surface being used.
��~�u8}s4� LoadAnalysis anaSurfNode, ana
�n<�CJx+�U �� b6S�86> 'Move the detector custom element to the desired z position.
N)�RWC7th{ z = 50
hC]c
=$�=7 GetOperation detNode,1,move
_d��s�d{&� move.Type = "Shift"
~>D;2 S�(a move.val3 = z
c0<Y017�sG SetOperation detNode,1,move
�{H $�\�, Print "New screen position, z = " &z
8M�g4y1)RU �;lX��:�EU 'Update the model and trace rays.
�v�!���@/� EnableTextPrinting (False)
�Q�|gu�n} Update
%8$J�L�=c� DeleteRays
R�^]��(X*� TraceCreateDraw
2k"�a%�#H8 EnableTextPrinting (True)
�WGG|d)�'@ z}C#�+VhQ` 'Calculate the irradiance for rays on the detector surface.
�>o 3X���) raysUsed = Irradiance( detSurfNode, -1, ana, irrad )
�tb/u@}"�) Print raysUsed & " rays were included in the irradiance calculation.
v.�6"�<nT2 4>Uo0NfL�� 'When using real number data to send to MATLAB, it is simplest to use PutWorkspaceData.
�<l wI|��< Matlab.PutWorkspaceData("irradiance_pwd","base",irrad)
#TW$J/Jb�� (�fh:q�2E# 'PutFullMatrix is more useful when actually having complex data such as with
>Fx�$R�ty� 'scalar wavefield, for example. Note that the scalarfield array in MATLAB
cw"x0 �RS 'is a complex valued array.
Z�
m��i<Z raysUsed = ScalarField ( detSurfNode, -1, ana, reals, imags )
�o�;��];ng Matlab.PutFullMatrix("scalarfield","base", reals, imags )
N>ct`a)BD/ Print raysUsed & " rays were included in the scalar field calculation."
lu��(�G3T8 ���7R)�)(- 'Calculate plot characteristics from the T_ANALYSIS structure. This information is used
�m�Sw��OP� 'to customize the plot figure.
tsfOPth$*� xMin = ana.posX+ana.AcellX*(ana.Amin-0.5)
�
� �|J�(] xMax = ana.posX+ana.AcellX*(ana.Amax+0.5)
FN,0&D��}` yMin = ana.posY+ana.BcellY*(ana.Bmin-0.5)
�:1�F�m~'� yMax = ana.posY+ana.BcellY*(ana.Bmax+0.5)
2z�0HB+Y}x nXpx = ana.Amax-ana.Amin+1
h%��=�b�"x nYpx = ana.Bmax-ana.Bmin+1
����N�%r}0 lBG*��P>; 'Plot the data in Matlab with some parameters calculated from the T_ANALYSIS
}�lpc���bm 'structure. Set the axes labels, title, colorbar and plot view.
��~O1��*�] Matlab.Execute( "figure; surf(linspace("&xMin &","&xMax &","&nXpx &"),linspace("& yMin &"," & yMax & "," & nYpx & "),irradiance_pwd, 'EdgeColor', 'None');" )
�#(aROTV5a Matlab.Execute( "xlabel('X Position (" & GetUnits() & ")')" ) : Matlab.Execute( "ylabel('Y Position (" & GetUnits() & ")')" ) : Matlab.Execute( "zLabel( 'Irradiance' )" )
i6���`8y�w Matlab.Execute( "title('Detector Irradiance')" )
"mPa�>`?�� Matlab.Execute( "colorbar" )
�s�Wavxh8A Matlab.Execute( "view(2)" )
1�v2wP2]|; Print ""
t_]UseP$RF Print "Matlab figure plotted..."
m\T�q0cT�$ 8!U�Z.���. 'Have Matlab calculate and return the mean value.
)&dhE�^
�O Matlab.Execute( "irrad = mean(mean(irradiance_pwd));" )
G�~B�
V�^� Matlab.GetWorkspaceData( "irrad", "base", meanVal )
(�
?/0$�DB Print "The mean irradiance value calculated by Matlab is: " & meanVal
�huKz["]z[ Plq��[Ml9
'Release resources
=r-�Wy.�a@ Set Matlab = Nothing
mu{%%�b7|^ �JyB>�,t) End Sub
�lZ)u�4_� |%RF��XkHS 最后在Matlab画图如下:
~-:��C�N(U nr-�mf]W&
并在工作区保存了数据:
4t�u�EC-oh 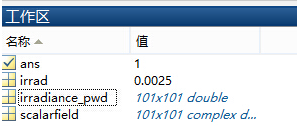 ~3�6�c0 �=
~3�6�c0 �= 并返回平均值:
\pzvo�j7�{ &y(aBy�I y 与FRED中计算的照度图对比:
S�D.�z�e(P epG;=\f}m` 例:
�NXmj<azED c=b\9!hr_E 此例
系统数据,可按照此数据建立
模型 ~�I�qT���> �zc�Z��w�} 系统数据
]cA~%$c89s i@I��%$!cB %@xYg��{�� 光源数据:
�S}<
<jI-z Type: Laser Beam(Gaussian 00 mode)
xK
���y<o� Beam size: 5;
[K�E4wz+s{ Grid size: 12;
jU#%�@d6!# Sample pts: 100;
;<�][upn� 相干光;
.���N'UnKz 波长0.5876微米,
f�Z376Z:S$ 距离原点沿着Z轴负方向25mm。
<�Q�kfvK]Q [`b{eLCFX] 对于执行代码,如果想保存图片,请在开始之前一定要执行如下代码:
C=b5[, UCB enableservice('AutomationServer', true)
Qdn��:4yk� enableservice('AutomationServer')