GGp{b>E+
# 简介:
FRED作为COM组件可以实现与Excel、VB、
Matlab等调用来完成庞大的计算任务或画图,本文的目的是通过运行一个案例来实现与Matlab的相互调用,在此我们需要借助脚本来完成,此脚本为视为通用型脚本。
��|thad�!? ]p}#N��Pe5 配置:在执行调用之前,我们需要在Matlab命令行窗口输入如下命令:
h����%/ssB enableservice('AutomationServer', true)
-2z,cj�&E{ enableservice('AutomationServer')
�n�'��B�mz 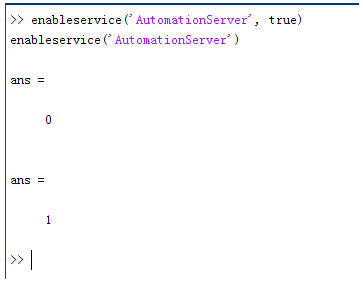 }o�V�3EI�H
}o�V�3EI�H 结果输出为1,这种操作方式保证了当前的Matlab实体可以用于
通信。
!2wETs�?� |C|�:i@c
H 在winwrp界面,为增加和使用Matlab类型的目录库,我们需要如下步骤:
h�9U+�%=^O 1. 在FRED脚本编辑界面找到参考.
,Z�?m��`cx 2. 找到Matlab Automation Server Type Library
9�Dy)nm^�� 3. 将名字改为MLAPP
>Rr!rtc'�x l-�F�mn/�V �c�J2y��)` 在Matlab里面有两种常用的数据发送选项PutWorkspaceData 及PutFullMatrix,PutWorkspaceData适用于存储一般的数据在工作区,并赋予其为变量,PutFullMatrix试用于复数数据。
y3Y2�QC�( 图 编辑/参考
i{P%{�hVb� VmMh+)��UZ #*+;B9�3�) 现在将脚本代码公布如下,此脚本执行如下几个步骤:
eC.w?(�RB 1. 创建Matlab服务器。
�@{'o#E�JY 2. 移动探测面对于前一聚焦面的位置。
ZH�b7����+ 3. 在探测面追迹
光线 �'}@e5^�oL 4. 在探测面计算
照度 �:82�?'aR� 5. 使用PutWorkspaceData发送照度数据到Matlab
f<�^ScF�VR 6. 使用PutFullMatrix发送标量场数据到Matlab中
�OX�`�?<@6 7. 用Matlab画出照度数据
�Z0{�f� 8. 在Matlab计算照度平均值
2NyUmJ�42� 9. 返回数据到FRED中
%;'~%\|dZM Z�b}`�s�k# 代码分享:
k:`a�+L�iZ cxL,]2�7Bu Option Explicit
>}70�]dN7b *>G�^!�e.u Sub Main
Io2��,% !D 5s#R`o��%Z Dim ana As T_ANALYSIS
�b_q!��>&c Dim move As T_OPERATION
zI1(F�67d` Dim Matlab As MLApp.MLApp
/7.w�Qe�L9 Dim detNode As Long, detSurfNode As Long, anaSurfNode As Long
s�Yl&Q.�\q Dim raysUsed As Long, nXpx As Long, nYpx As Long
��3&O%� & Dim irrad() As Double, imagData() As Double, reals() As Double, imags() As Double
eB)�UXOu1 Dim z As Double, xMin As Double, xMax As Double, yMin As Double, yMax As Double
�sV]i�/��B Dim meanVal As Variant
~}ep�q�6L> 5%EaX�?0h+ Set Matlab = CreateObject("Matlab.Application")
[SKP�|`I>I ^ b=5 6~[ ClearOutputWindow
2Y9y5[K,F) �M�ac�L3f 'Find the node numbers for the entities being used.
;�|�Y2r^�c detNode = FindFullName("Geometry.Screen")
Ar\IZ_Q� detSurfNode = FindFullName("Geometry.Screen.Surf 1")
�I�|GV
:�D anaSurfNode = FindFullName("Analysis Surface(s).Analysis 1")
6w�a�<'!�� { +i;��e]c 'Load the properties of the analysis surface being used.
s4^[3|Zrr0 LoadAnalysis anaSurfNode, ana
�f<Va<TL6- "(9=h@@Y"� 'Move the detector custom element to the desired z position.
P9 W�<�gIO z = 50
�m�Mel,iK= GetOperation detNode,1,move
U{��j�5k�X move.Type = "Shift"
�pyu46iE�) move.val3 = z
�---Ks0\V� SetOperation detNode,1,move
n�C-�c�8�y Print "New screen position, z = " &z
T3��=-UYx] N:m@D][/sW 'Update the model and trace rays.
�s?4%<�j�z EnableTextPrinting (False)
}Z~pfm_��S Update
8�#[�%?}tK DeleteRays
f�(E�Yx)gZ TraceCreateDraw
m0dF�A�<5- EnableTextPrinting (True)
��K8e4a�x� @���h�,h=X 'Calculate the irradiance for rays on the detector surface.
(:t�Tx>V�# raysUsed = Irradiance( detSurfNode, -1, ana, irrad )
WM�~�J,`]J Print raysUsed & " rays were included in the irradiance calculation.
sa\|"IkD2� Requ.?!fG; 'When using real number data to send to MATLAB, it is simplest to use PutWorkspaceData.
%!�N2!IiVs Matlab.PutWorkspaceData("irradiance_pwd","base",irrad)
'������l�Q Q'
OuZKhA� 'PutFullMatrix is more useful when actually having complex data such as with
NgD�Z4&��L 'scalar wavefield, for example. Note that the scalarfield array in MATLAB
�f�(w#LuW< 'is a complex valued array.
�/6Jy'"+'0 raysUsed = ScalarField ( detSurfNode, -1, ana, reals, imags )
�j]�c�XLY
Matlab.PutFullMatrix("scalarfield","base", reals, imags )
V1UUAvN�7s Print raysUsed & " rays were included in the scalar field calculation."
��=�R"Eb1 �D}k-2RM2k 'Calculate plot characteristics from the T_ANALYSIS structure. This information is used
�.:#_�5�K 'to customize the plot figure.
s[�vPH8�qb xMin = ana.posX+ana.AcellX*(ana.Amin-0.5)
W�(��]E04� xMax = ana.posX+ana.AcellX*(ana.Amax+0.5)
RE(=! 8lGR yMin = ana.posY+ana.BcellY*(ana.Bmin-0.5)
�B.C�H9�M� yMax = ana.posY+ana.BcellY*(ana.Bmax+0.5)
KoxGxHz^Y3 nXpx = ana.Amax-ana.Amin+1
y�hJA;&�}> nYpx = ana.Bmax-ana.Bmin+1
4{Yy05PFS� oF 1W�}DtA 'Plot the data in Matlab with some parameters calculated from the T_ANALYSIS
b7�>,�-O�� 'structure. Set the axes labels, title, colorbar and plot view.
{7��ZtOe�� Matlab.Execute( "figure; surf(linspace("&xMin &","&xMax &","&nXpx &"),linspace("& yMin &"," & yMax & "," & nYpx & "),irradiance_pwd, 'EdgeColor', 'None');" )
0C"PC:�h5� Matlab.Execute( "xlabel('X Position (" & GetUnits() & ")')" ) : Matlab.Execute( "ylabel('Y Position (" & GetUnits() & ")')" ) : Matlab.Execute( "zLabel( 'Irradiance' )" )
l�&e�5_]+% Matlab.Execute( "title('Detector Irradiance')" )
$)k�Bz*C�[ Matlab.Execute( "colorbar" )
�H�L}�sqcp Matlab.Execute( "view(2)" )
E'Fv *UA�� Print ""
3��_�R ��� Print "Matlab figure plotted..."
#buV;!_!E? h1G��*y��� 'Have Matlab calculate and return the mean value.
xqi�*N1�3� Matlab.Execute( "irrad = mean(mean(irradiance_pwd));" )
!?us[f=g%� Matlab.GetWorkspaceData( "irrad", "base", meanVal )
{{�4p��{� Print "The mean irradiance value calculated by Matlab is: " & meanVal
.�5#t��B*H ������`lV 'Release resources
��f2SU�5e2 Set Matlab = Nothing
+��UpMMh q �:<WQ�;q�� End Sub
-K����U)7V �f�a*H� cz 最后在Matlab画图如下:
0��8d_DC�R 6iV"Tl{�z- 并在工作区保存了数据:
?( d�YW7S  NP�<�F==,
NP�<�F==, 并返回平均值:
C&�CsI] @g $�<>EwW� 与FRED中计算的照度图对比:
yB��D��2�� &xi�D�G=I# 例:
_:fO)�gs|1 :�+��%h��� 此例
系统数据,可按照此数据建立
模型 ��X�
�gx2� 9Sj:nn^/u 系统数据
8�.�;';[� &T�|&D[�@� �dbq���{a� 光源数据:
E23�� Yk?" Type: Laser Beam(Gaussian 00 mode)
Rm\�']�;� Beam size: 5;
,Q ��/�nS$ Grid size: 12;
/�Vm}+"BCS Sample pts: 100;
L/�iV�s`qF 相干光;
<@�AsCiQF 波长0.5876微米,
pJ*#aH[ySP 距离原点沿着Z轴负方向25mm。
:?:j$
=nWN v�<J;S9u=� 对于执行代码,如果想保存图片,请在开始之前一定要执行如下代码:
gt �t��$O� enableservice('AutomationServer', true)
DP6{HR��$L enableservice('AutomationServer')