DG:=E/���@ 简介:
FRED作为COM组件可以实现与Excel、VB、
Matlab等调用来完成庞大的计算任务或画图,本文的目的是通过运行一个案例来实现与Matlab的相互调用,在此我们需要借助脚本来完成,此脚本为视为通用型脚本。
$�~:h��v7% �F�t>�ix�n 配置:在执行调用之前,我们需要在Matlab命令行窗口输入如下命令:
_�aD�x�('
enableservice('AutomationServer', true)
~Y�r.0i.�W enableservice('AutomationServer')
�0c�3G_I=� 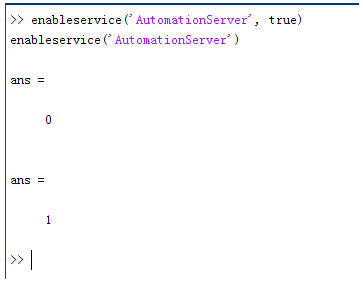 �Jx�{,x�-I
�Jx�{,x�-I 结果输出为1,这种操作方式保证了当前的Matlab实体可以用于
通信。
2X��I�%�4 �)�E4C�Ow+ 在winwrp界面,为增加和使用Matlab类型的目录库,我们需要如下步骤:
#)���;
6+v 1. 在FRED脚本编辑界面找到参考.
,U7hzBj8k� 2. 找到Matlab Automation Server Type Library
�AVcZ.�+�? 3. 将名字改为MLAPP
st+Kz ��uK xeHu-J!P�� gq0�g���r? 在Matlab里面有两种常用的数据发送选项PutWorkspaceData 及PutFullMatrix,PutWorkspaceData适用于存储一般的数据在工作区,并赋予其为变量,PutFullMatrix试用于复数数据。
#�JW1J�CT
图 编辑/参考
b�u�hxC5i% 7P��\s�n<� Yb�6\+�}th 现在将脚本代码公布如下,此脚本执行如下几个步骤:
_n_i*p�
'2 1. 创建Matlab服务器。
qh&K{r�*�T 2. 移动探测面对于前一聚焦面的位置。
~�c�Z1=,�P 3. 在探测面追迹
光线 []Fy[G�.)H 4. 在探测面计算
照度 s�nK9']WXo 5. 使用PutWorkspaceData发送照度数据到Matlab
I+<;�D�sp� 6. 使用PutFullMatrix发送标量场数据到Matlab中
#�#n\�9ipD 7. 用Matlab画出照度数据
Qy$QOtr��v 8. 在Matlab计算照度平均值
Z7���f~|}� 9. 返回数据到FRED中
t�)�m4"p�7 ?_�^9�e��� 代码分享:
J`�V6zGgW� V2y[IeS�Q Option Explicit
DMf9�w�B B�o0y"W�[+ Sub Main
j�xoEOEA� A9R}74e�4g Dim ana As T_ANALYSIS
�m�0#hG
x Dim move As T_OPERATION
�x��[?�_F� Dim Matlab As MLApp.MLApp
e���U1�2*( Dim detNode As Long, detSurfNode As Long, anaSurfNode As Long
/J6��CSk�� Dim raysUsed As Long, nXpx As Long, nYpx As Long
EP8LJ�zd"� Dim irrad() As Double, imagData() As Double, reals() As Double, imags() As Double
1r�KR��=To Dim z As Double, xMin As Double, xMax As Double, yMin As Double, yMax As Double
asJYGq��dF Dim meanVal As Variant
<T}#>xHs�3 O@$hG��8:� Set Matlab = CreateObject("Matlab.Application")
�tT
v@8f�� \.{JS>�!�� ClearOutputWindow
�%*/[aq,�# ._R82���gy 'Find the node numbers for the entities being used.
3a��5H<3w_ detNode = FindFullName("Geometry.Screen")
>:xnjEsi$/ detSurfNode = FindFullName("Geometry.Screen.Surf 1")
F�0�!r9U(( anaSurfNode = FindFullName("Analysis Surface(s).Analysis 1")
F?dT�C�a�� kQb0��pfYs 'Load the properties of the analysis surface being used.
s R~&�S�)) LoadAnalysis anaSurfNode, ana
��BN�ByaC� �^g0 I�g2' 'Move the detector custom element to the desired z position.
�ysa"f�+/ z = 50
�e��Jwr�� GetOperation detNode,1,move
���~\/� J& move.Type = "Shift"
4H,DG`�[Mo move.val3 = z
-`;8~�w�MN SetOperation detNode,1,move
s��,}<5N]U Print "New screen position, z = " &z
jmb\eOq+~V .�SsIU�\[) 'Update the model and trace rays.
f�&`*x �t/ EnableTextPrinting (False)
U!'l�c}��5 Update
u1��"e+4f� DeleteRays
646ye�Q��1 TraceCreateDraw
+-Dd*y�D6< EnableTextPrinting (True)
mSzwx�/�3" n�FP2wv�FM 'Calculate the irradiance for rays on the detector surface.
�M{S�7ia"s raysUsed = Irradiance( detSurfNode, -1, ana, irrad )
dnx}�c�4P� Print raysUsed & " rays were included in the irradiance calculation.
�V?"^Ff3m! �6�M6�QMg^ 'When using real number data to send to MATLAB, it is simplest to use PutWorkspaceData.
4 hj2�rK'y Matlab.PutWorkspaceData("irradiance_pwd","base",irrad)
Q(s�bClp"� X1-s,[��j' 'PutFullMatrix is more useful when actually having complex data such as with
��d�b�LX}> 'scalar wavefield, for example. Note that the scalarfield array in MATLAB
k`t'P�6
bU 'is a complex valued array.
�j@ "`!uPz raysUsed = ScalarField ( detSurfNode, -1, ana, reals, imags )
�.��
9
NS Matlab.PutFullMatrix("scalarfield","base", reals, imags )
9,Mp/.T"�\ Print raysUsed & " rays were included in the scalar field calculation."
*HC8kD a%$ cU>�&E*�wD 'Calculate plot characteristics from the T_ANALYSIS structure. This information is used
V�;6M[�ic} 'to customize the plot figure.
bDkE�*4SRX xMin = ana.posX+ana.AcellX*(ana.Amin-0.5)
ZChY:I$�<� xMax = ana.posX+ana.AcellX*(ana.Amax+0.5)
��`8-aHPF- yMin = ana.posY+ana.BcellY*(ana.Bmin-0.5)
5B��2,=?+o yMax = ana.posY+ana.BcellY*(ana.Bmax+0.5)
(H��F,p,h_ nXpx = ana.Amax-ana.Amin+1
�4"2/"D��0 nYpx = ana.Bmax-ana.Bmin+1
4Rm3��'�Ch C0W~Tk\C�2 'Plot the data in Matlab with some parameters calculated from the T_ANALYSIS
SQ!lgm1bA 'structure. Set the axes labels, title, colorbar and plot view.
A)#�sh)
}Q Matlab.Execute( "figure; surf(linspace("&xMin &","&xMax &","&nXpx &"),linspace("& yMin &"," & yMax & "," & nYpx & "),irradiance_pwd, 'EdgeColor', 'None');" )
��w(U/(C7R Matlab.Execute( "xlabel('X Position (" & GetUnits() & ")')" ) : Matlab.Execute( "ylabel('Y Position (" & GetUnits() & ")')" ) : Matlab.Execute( "zLabel( 'Irradiance' )" )
+wSm6�*j7= Matlab.Execute( "title('Detector Irradiance')" )
VB#31T#�q? Matlab.Execute( "colorbar" )
�v���P4Ij� Matlab.Execute( "view(2)" )
cg.e�(@(� Print ""
oL�@�ou{iQ Print "Matlab figure plotted..."
>�(CoX�SV5 S3'g�(+��S 'Have Matlab calculate and return the mean value.
Fs|;>Up0�� Matlab.Execute( "irrad = mean(mean(irradiance_pwd));" )
E
oR�(/*' Matlab.GetWorkspaceData( "irrad", "base", meanVal )
��'k6�7$H� Print "The mean irradiance value calculated by Matlab is: " & meanVal
P�~<�9��3 rr�W��k&;? 'Release resources
9c^EoY�py- Set Matlab = Nothing
5%���`Ul� J9FNjM�[qe End Sub
ZX;k*Or�W� 55�Dz�BV�� 最后在Matlab画图如下:
xdM��#>z`; _e�_%�U<\4 并在工作区保存了数据:
w'0M�>2��� 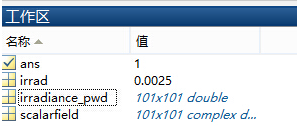 UT�~2}B9fc
UT�~2}B9fc 并返回平均值:
(3h*sd5�ly @>@Nu�g2 � 与FRED中计算的照度图对比:
gk��1��S"H �WS�/+Y��l 例:
\���Sby(l� �5�5�LF��� 此例
系统数据,可按照此数据建立
模型 UK>=�y_FYO �P`
F'Nf2U 系统数据
)�T5h\ZO`; @>Ijf�rjV� "T
�u[n\8 光源数据:
mv?H��]i`N Type: Laser Beam(Gaussian 00 mode)
k�V3j}C"�� Beam size: 5;
mJ>9�9:W+� Grid size: 12;
E`n`#�=xKR Sample pts: 100;
Pu*HZW�3l� 相干光;
k#5�e:VOb� 波长0.5876微米,
p.]� .M�"A 距离原点沿着Z轴负方向25mm。
��bMZ�n7c� 2P�_�^��@g 对于执行代码,如果想保存图片,请在开始之前一定要执行如下代码:
Z�{4aG�p* enableservice('AutomationServer', true)
n�E0�~�Y�2 enableservice('AutomationServer')