-
UID:317649
-
- 注册时间2020-06-19
- 最后登录2025-09-29
- 在线时间1866小时
-
-
访问TA的空间加好友用道具

|
简介:FRED作为COM组件可以实现与Excel、VB、Matlab等调用来完成庞大的计算任务或画图,本文的目的是通过运行一个案例来实现与Matlab的相互调用,在此我们需要借助脚本来完成,此脚本为视为通用型脚本。 pw(U< �)�� A{�{q'zb�! 配置:在执行调用之前,我们需要在Matlab命令行窗口输入如下命令: ?%8})^Dd>4 enableservice('AutomationServer', true) �5VoOJ_h�q enableservice('AutomationServer') )Rm
�'Ym�O 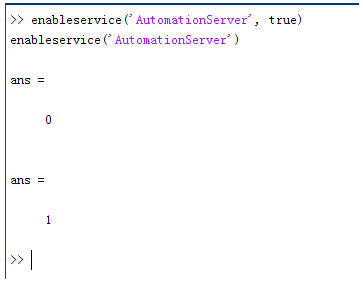 Z!s>AgH9�u 结果输出为1,这种操作方式保证了当前的Matlab实体可以用于通信。 f:JYG]E��& W�?4&�lC^G 在winwrp界面,为增加和使用Matlab类型的目录库,我们需要如下步骤:
mZ& \3m�= 1. 在FRED脚本编辑界面找到参考. R~x��;X�3� 2. 找到Matlab Automation Server Type Library D� x��>1�y 3. 将名字改为MLAPP *x#��&��[> ;/hH=I�T� z9);�e�8ck 在Matlab里面有两种常用的数据发送选项PutWorkspaceData 及PutFullMatrix,PutWorkspaceData适用于存储一般的数据在工作区,并赋予其为变量,PutFullMatrix试用于复数数据。 CHdet(�_=v �0T�n|Q9R� Z!s>AgH9�u 结果输出为1,这种操作方式保证了当前的Matlab实体可以用于通信。 f:JYG]E��& W�?4&�lC^G 在winwrp界面,为增加和使用Matlab类型的目录库,我们需要如下步骤:
mZ& \3m�= 1. 在FRED脚本编辑界面找到参考. R~x��;X�3� 2. 找到Matlab Automation Server Type Library D� x��>1�y 3. 将名字改为MLAPP *x#��&��[> ;/hH=I�T� z9);�e�8ck 在Matlab里面有两种常用的数据发送选项PutWorkspaceData 及PutFullMatrix,PutWorkspaceData适用于存储一般的数据在工作区,并赋予其为变量,PutFullMatrix试用于复数数据。 CHdet(�_=v �0T�n|Q9R� 图 编辑/参考 �&E�bD.>Ci YWn6wzu%Vc 现在将脚本代码公布如下,此脚本执行如下几个步骤: �U{z�a m 1. 创建Matlab服务器。 aQym=
6�%e 2. 移动探测面对于前一聚焦面的位置。 R�;�G��l�{ 3. 在探测面追迹光线 .9[8H�:Fe� 4. 在探测面计算照度 X T)h�Pwg. 5. 使用PutWorkspaceData发送照度数据到Matlab X{9JS���q� 6. 使用PutFullMatrix发送标量场数据到Matlab中 '��nj&}�A' 7. 用Matlab画出照度数据 mw4'z,�1Q 8. 在Matlab计算照度平均值 B�1i!te�}* 9. 返回数据到FRED中 Mh-�*5R��x �5LhJ�8$�W 代码分享: ]%Q]C
8[�C kgbr+Yw2X� Option Explicit �{pQ@0�b ~g�LEh��tW Sub Main YVg}q#���
+(�h6{e%) Dim ana As T_ANALYSIS wEH�re��r Dim move As T_OPERATION O(�
5L2G�� Dim Matlab As MLApp.MLApp t�$�PnQ@xu Dim detNode As Long, detSurfNode As Long, anaSurfNode As Long q3pN/f;kr, Dim raysUsed As Long, nXpx As Long, nYpx As Long �}5Tyz��i( Dim irrad() As Double, imagData() As Double, reals() As Double, imags() As Double ��l)!�woOt Dim z As Double, xMin As Double, xMax As Double, yMin As Double, yMax As Double z�N8V��~M; Dim meanVal As Variant {p��� lmFV luxK�g�c�U Set Matlab = CreateObject("Matlab.Application") >�-��tH&X^ w�or'=byh\ ClearOutputWindow �Ki�Rt�'� Rc�x�'a�:k 'Find the node numbers for the entities being used. G��Yb2m"a) detNode = FindFullName("Geometry.Screen") >.�nt�'BQ detSurfNode = FindFullName("Geometry.Screen.Surf 1") OS�h mrz28 anaSurfNode = FindFullName("Analysis Surface(s).Analysis 1") �Qig�!NgOM M]/�we�i"X 'Load the properties of the analysis surface being used. 5�2C-D+zCJ LoadAnalysis anaSurfNode, ana `�S~@�F�X ]JCB^�)t�M 'Move the detector custom element to the desired z position. DR�g��~HT� z = 50 VOF:�+o@. GetOperation detNode,1,move .Zo9�^0`C� move.Type = "Shift" ��__zu-�!v move.val3 = z YT%�SC�aU� SetOperation detNode,1,move 5�SW�X �v+ Print "New screen position, z = " &z {msB+n�~WZ m$y$wo<K[7 'Update the model and trace rays. �6x�3Ew2�� EnableTextPrinting (False) t�-|�=weNy Update ���[\%t<aa DeleteRays &=��yqWW?� TraceCreateDraw WZ
V�*J�& EnableTextPrinting (True) /$4?�.qt�u u��Y%3X/^j 'Calculate the irradiance for rays on the detector surface. <x;[� H%� raysUsed = Irradiance( detSurfNode, -1, ana, irrad ) Y�U�\t+�/b Print raysUsed & " rays were included in the irradiance calculation.
T9;o�.f S }m
l�bN0v 'When using real number data to send to MATLAB, it is simplest to use PutWorkspaceData. z�'}t@�R#H Matlab.PutWorkspaceData("irradiance_pwd","base",irrad) C00*X[��p 3z�. �>b 'PutFullMatrix is more useful when actually having complex data such as with f'yd�{ihFp 'scalar wavefield, for example. Note that the scalarfield array in MATLAB 9NoPrR=x�1 'is a complex valued array. (�����L��� raysUsed = ScalarField ( detSurfNode, -1, ana, reals, imags ) Mn�{Rg�>�X Matlab.PutFullMatrix("scalarfield","base", reals, imags ) JI; i1@|�b Print raysUsed & " rays were included in the scalar field calculation." c94�PW�PU� /�n}�V7��� 'Calculate plot characteristics from the T_ANALYSIS structure. This information is used fq!6#Usf;i 'to customize the plot figure. @�5@{�Es1u xMin = ana.posX+ana.AcellX*(ana.Amin-0.5) ��7Sv5fLu2 xMax = ana.posX+ana.AcellX*(ana.Amax+0.5) �x=r6�vOj� yMin = ana.posY+ana.BcellY*(ana.Bmin-0.5) >�0ok�b�3+ yMax = ana.posY+ana.BcellY*(ana.Bmax+0.5) 3�Eu�x-C!t nXpx = ana.Amax-ana.Amin+1 DppvUiQB!a nYpx = ana.Bmax-ana.Bmin+1 ,&l��*AB�! G� u��I sM 'Plot the data in Matlab with some parameters calculated from the T_ANALYSIS w`Aw�+[24� 'structure. Set the axes labels, title, colorbar and plot view. <6@NgSFz'� Matlab.Execute( "figure; surf(linspace("&xMin &","&xMax &","&nXpx &"),linspace("& yMin &"," & yMax & "," & nYpx & "),irradiance_pwd, 'EdgeColor', 'None');" ) [5#/&�k{�� Matlab.Execute( "xlabel('X Position (" & GetUnits() & ")')" ) : Matlab.Execute( "ylabel('Y Position (" & GetUnits() & ")')" ) : Matlab.Execute( "zLabel( 'Irradiance' )" ) 2&f�=�4b`Z Matlab.Execute( "title('Detector Irradiance')" ) �\z���?;6A Matlab.Execute( "colorbar" ) �6Kc7@oO�~ Matlab.Execute( "view(2)" ) U`�4Z�j1�y Print "" ;�+Ke�wi;< Print "Matlab figure plotted..." aRKG)��0�= M@8�6u^�80 'Have Matlab calculate and return the mean value. 8[p6�C Jl) Matlab.Execute( "irrad = mean(mean(irradiance_pwd));" ) cG"�<*Xi�< Matlab.GetWorkspaceData( "irrad", "base", meanVal ) I8�>��1RXz Print "The mean irradiance value calculated by Matlab is: " & meanVal *i�N]#)3>� Mj;'vm7#'� 'Release resources )bg,rES�M� Set Matlab = Nothing 6Z}))�*3 9 �l�;FgX�+) End Sub jJnB�wH��p i�-�W2!;�G 最后在Matlab画图如下: �{v'F���g� �JEkV�j']? 并在工作区保存了数据: lL�f01sa4� [uV/ Ra*g�  b,A1(_p�zi b,A1(_p�zi
�cO+`�8`kv 与FRED中计算的照度图对比: z,P7b]KVe� wZb�@V�G}% 例: hfc!M2/�w c$z_Zi!g#� 此例系统数据,可按照此数据建立模型 ��W�5�;sps
/;ITn���G� 系统数据 �![�n`n(oN
/ /�rWc,�c �nuA�!Jln_ 光源数据: o~��>go_�Y Type: Laser Beam(Gaussian 00 mode) �a�N3�{\�^ Beam size: 5; ���C�#�0Wo Grid size: 12; ^��}�L$[P� Sample pts: 100; �#��n�hAW� 相干光; u^p[z�epW\ 波长0.5876微米, F�Z/&[�;E! 距离原点沿着Z轴负方向25mm。 �[: j_Y3-9 wQ.zj`�?$( 对于执行代码,如果想保存图片,请在开始之前一定要执行如下代码: Ut�=�y`]F enableservice('AutomationServer', true) L�+�CSF ]� enableservice('AutomationServer') �SQ�k!�o{ �SQ�k!�o{
|